UNDERFLOOR HEATING
Topics:
– Types of underfloor heating systems
– Hydronic systems
– Hydronic system adventages
– Pipe layout strategy and heat distribution
– Installation practices
Types of underfloor heating systems
Radiant floor heating is the oldest form of central heating and can be done in two ways:
– Hydronic systems – pumps warm water through piping under the floor (“wet system”)
Hydronic underfloor heating system will cost about a third more than a radiator system.
– Electric systems – electric coils placed under the floor (“dry system”)
Electric underfloor heating generally costs less to install, but is more expensive to run.
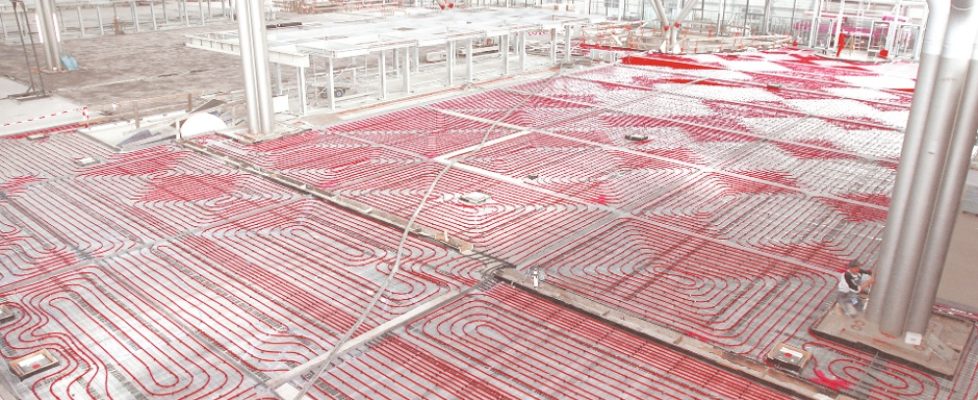
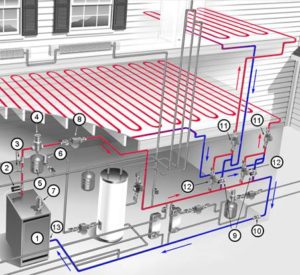
Hydronic systems
Hydronic systems use water or a mix of water and anti-freeze such as propylene glycol as the heat transfer fluid that is circulated between the floor and the boiler. Various types of pipes are available and they are generally made from polyethylene including PEX, PEX-Al-PEX and PERT. Older materials such as Polybutylene (PB) and copper or steel pipe are still used in some locales or for specialized applications.
Hydronic system adventages
The advantage of this method of heating is that it is cheaper for heating the whole house, and there are several ways to heat water:
Gas-fired boiler
Oil-fired boiler
Kerosene, gas or solar water heater
Maintenance for a hydronic system is minimal, the boiler needs an annual check-up, but most modern pumps use water to lubricate the parts and are low-maintenance.
Underfloor heating is commonly installed with stone, ceramic or terracotta tile floors, but can also be installed with wood, linoleum or carpet.
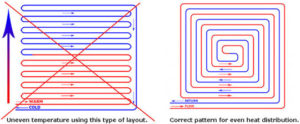
Pipe layout strategy and heat distribution
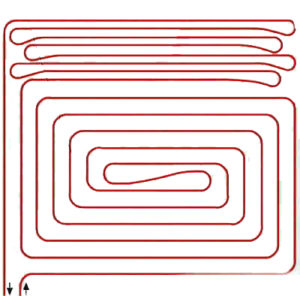
Meandering produces relatively uneven surface temperature distribution (for small and subordinate spaces and border zones).
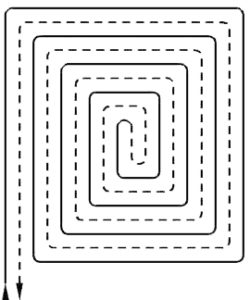
Placing pipes in the spiral (helical) layout, results in a uniform surface temperature over the entire room area, which has a positive effect on a subsequent change in the furnishings.
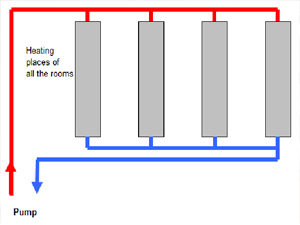
Tichelmann system is considered good solution in terms of energy efficiency – even temperature distribution. The Tichelmann principle is a simple way for balancing the hydronic system.
Based on the same arrangement of supply and return lines, it is easy to construct. It does not require additional control and has no moving parts that can cause defects or faults. This increases the operational safety of the plant.
The Tichelmann principle in simple words means that pipes are arranged in such manner that cold and hot water travel same length for each section on every floor.
Installation practices
A pipes packed closer together (less than 5”) is recommended to achieve a higher heat output at the edges to exterior walls or windows (especially for floor-level windows). This measure is intended to reduce the cold air, an important comfort criterion to meet.
Plastic pipes should always be endless so laid without joints. A minimum bending radius is observed so that the pipes are not kinked.